Overview
There are several patterns in software architectural part. And sometimes we might confuse to use which one. So I want to put the definition here ~
MVC
MVC(Model-View-Controller) is commonly used for developing user interfaces. It divide the related program logic into 3 interconnected elements.
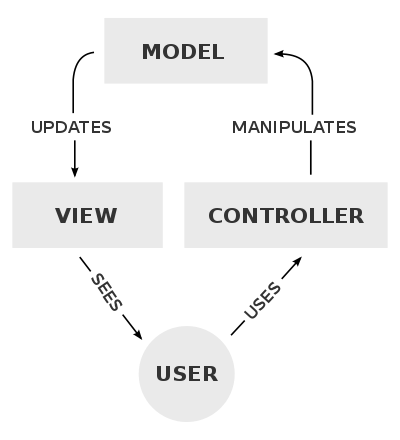
Model The central component of the pattern. It is the application’s dynamic data structure, independent of the user interface.[5] It directly manages the data, logic and rules of the application.
View Any representation of information such as a chart, diagram or table. Multiple views of the same information are possible, such as a bar chart for management and a tabular view for accountants.
Controller Accepts input and converts it to commands for the model or view.
- The model take responsibble to manage data of the application. It receive user input from controller.
- The view means presentation fo the model in particular format (UI)
- The controller responds to the user input and perform interactions on the data model objects. Controller receives the input and optionally validates it and then passes the input to the model.
MVP
MVP(Model-View-Presenter) is a derivation of MVC. It also devide into 3 elements.
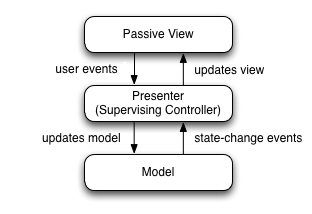
The model is an interface defining the data to be displayed or otherwise acted upon in the user interface.
The view is a passive interface that displays data (the model) and routes user commands (events) to the presenter to act upon that data.
The presenter acts upon the model and the view. It retrieves data from repositories (the model), and formats it for display in the view.
MVVM
MVVM(Model-View-ViewModel) facilitates a separation of development of GUI(graphical user interface). It also referred to as model-view-binder.
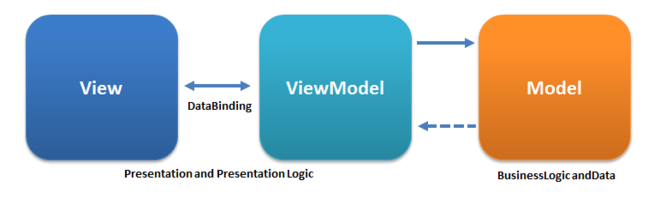
Model Model refers either to a domain model, which represents real state content (an object-oriented approach), or to the data access layer, which represents content (a data-centric approach).[citation needed]
View As in the model-view-controller (MVC) and model-view-presenter (MVP) patterns, the view is the structure, layout, and appearance of what a user sees on the screen. It displays a representation of the model and receives the user’s interaction with the view (clicks, keyboard, gestures, etc.), and it forwards the handling of these to the view model via the data binding (properties, event callbacks, etc.) that is defined to link the view and view model.
View model The view model is an abstraction of the view exposing public properties and commands. Instead of the controller of the MVC pattern, or the presenter of the MVP pattern, MVVM has a binder, which automates communication between the view and its bound properties in the view model. The view model has been described as a state of the data in the model. The main difference between the view model and the Presenter in the MVP pattern, is that the presenter has a reference to a view whereas the view model does not. Instead, a view directly binds to properties on the view model to send and receive updates. To function efficiently, this requires a binding technology or generating boilerplate code to do the binding.
Binder Declarative data and command-binding are implicit in the MVVM pattern. In the Microsoft solution stack, the binder is a markup language called XAML. The binder frees the developer from being obliged to write boiler-plate logic to synchronize the view model and view. When implemented outside of the Microsoft stack, the presence of a declarative data binding technology is what makes this pattern possible,[4][9] and without a binder, one would typically use MVP or MVC instead and have to write more boilerplate (or generate it with some other tool).
References
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Model–view–controller

Comments
Join the discussion for this article at here . Our comments is using Github Issues. All of posted comments will display at this page instantly.