Circular Queue is a linear data structure in which the operations are performed based on FIFO (First In First Out) principle and the last position is connected back to the first position to make a circle. It is also called ‘Ring Buffer’.
In normal Queue, we can insert element until queue becomes full. But once it got full, we cannot insert element even there is a space in front of queue. ex:
space 5
Queue: 3, 5, 7, 9, 13
even we pop 3, 5 later, we cannot insert new element into queue again
But this can be avoided by using Circular Queue:
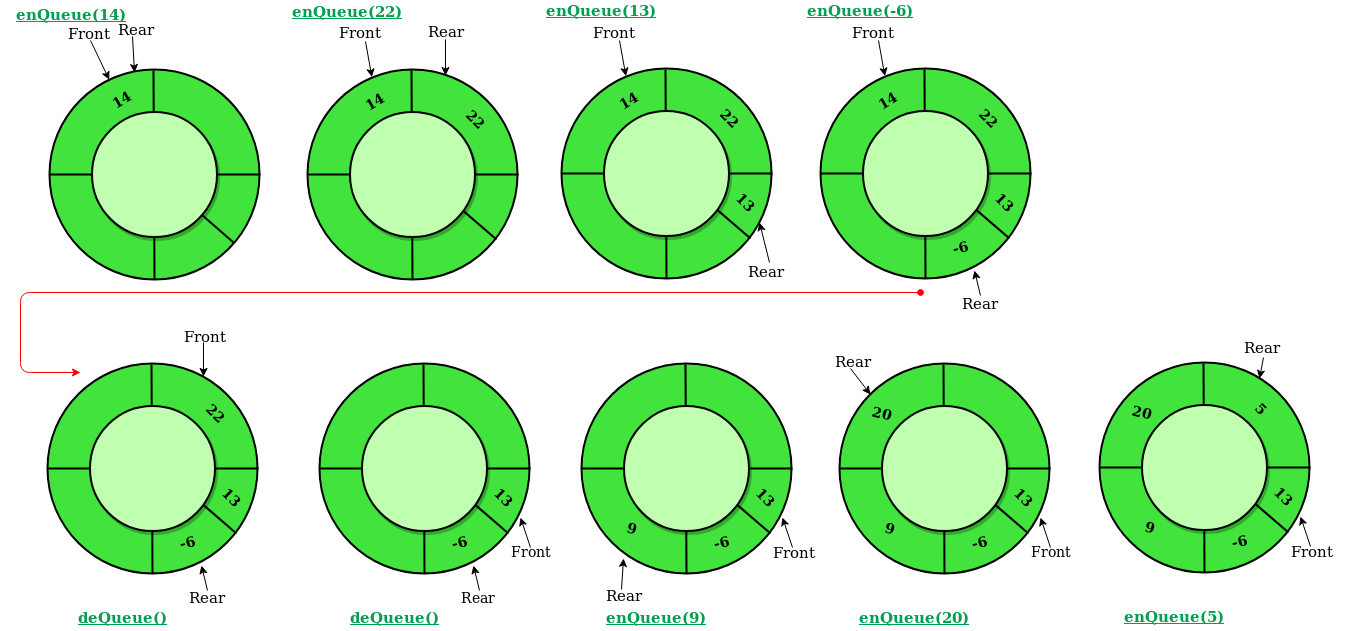
Operations
- Front: Get the front item from queue.
- Rear: Get the last item from queue.
- enQueue(value): This function is used to insert an element into the circular queue. In a circular queue, the new element is always inserted at Rear position.
- deQueue(): This function is used to delete an element from the circular queue. In a circular queue, the element is always deleted from front position.
- isEmpty(): Checks whether the circular queue is empty or not.
- isFull(): Checks whether the circular queue is full or not.
Swift Code
class MyCircularQueue {
var arr: [Int?]
var head: Int
var tail: Int
let n: Int
init(_ k: Int) {
arr = Array(repeating: nil, count: k)
head = 0
tail = 0
n = k
}
func enQueue(_ value: Int) -> Bool {
guard !isFull() else { return false }
if isEmpty() {
arr[head] = value
} else {
tail += 1
if tail == n {
tail = 0
}
arr[tail] = value
}
return true
}
func deQueue() -> Bool {
guard !isEmpty() else { return false }
arr[head] = nil
head += 1
if head == n {
head = 0
}
if isEmpty() {
// if there is no next element, move tail pointer together with head pointer
tail = head
}
return true
}
func Front() -> Int {
return isEmpty() ? -1 : arr[head]!
}
func Rear() -> Int {
return isEmpty() ? -1 : arr[tail]!
}
func isEmpty() -> Bool {
return arr[head] == nil
}
func isFull() -> Bool {
guard !isEmpty() else { return false }
if head <= tail {
return tail - head + 1 == n
} else {
return head == tail + 1
}
}
}
/**
* Your MyCircularQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* let obj = MyCircularQueue(k)
* let ret_1: Bool = obj.enQueue(value)
* let ret_2: Bool = obj.deQueue()
* let ret_3: Int = obj.Front()
* let ret_4: Int = obj.Rear()
* let ret_5: Bool = obj.isEmpty()
* let ret_6: Bool = obj.isFull()
*/

Comments
Join the discussion for this article at here . Our comments is using Github Issues. All of posted comments will display at this page instantly.