Load Balancer(LB) helps to spread the traffic across a cluster of servers to improve responsiveness and availability of applications, websites or databases. LB also keeps track of the status of all the resources while distributing requests. If server is not available to take new requests or is not responding or has elevated error rate. LB will stop sending traffic to such a server.
Normally a load balancer is put between client and server accepting incoming network and application traffic and distributing the traffic across multiple backend servers using various algorithms.
By balacing application requests across multiple servers, a load balancer reduces individual server load and prevents any one application server from becoming a single point of failure. Thus improving overall application availability and responsiveness.
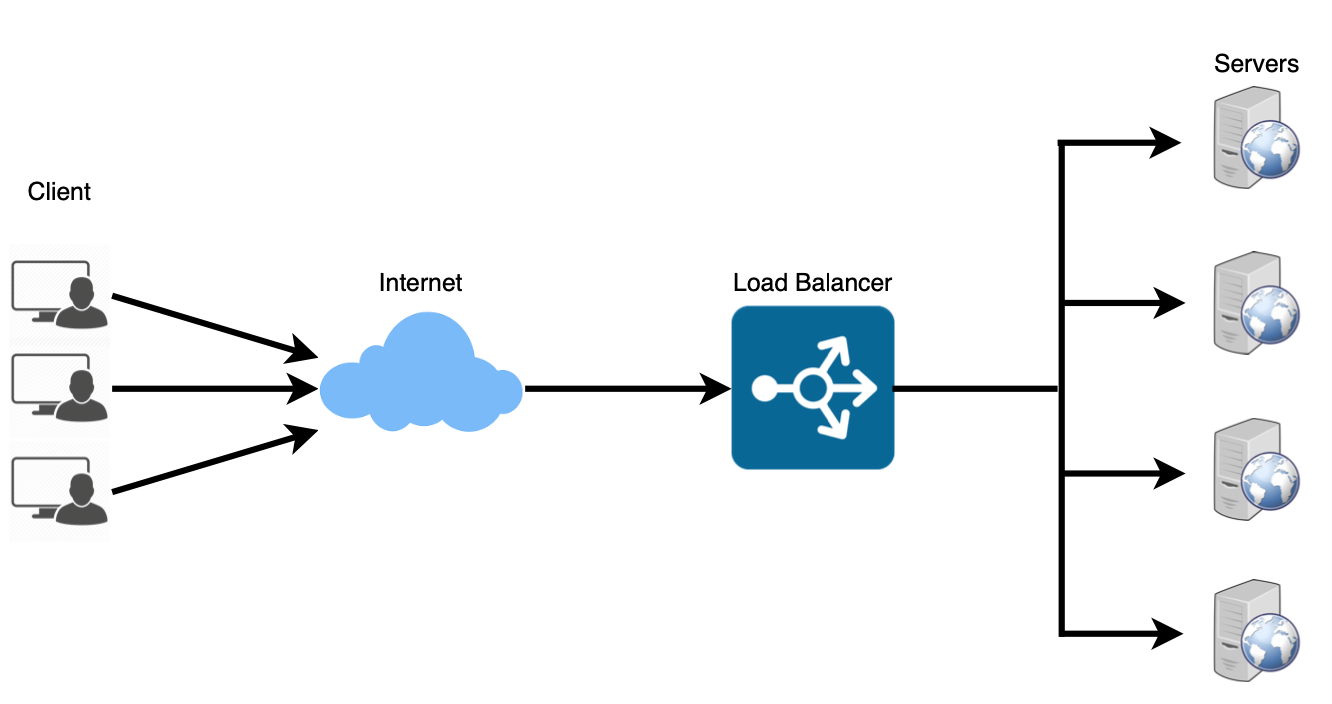
We could add LBs at three places:
- Between the user and the web server
- Between web server and an internal platform layer, ex: application servers or cache servers
- Between internal platform layer and database
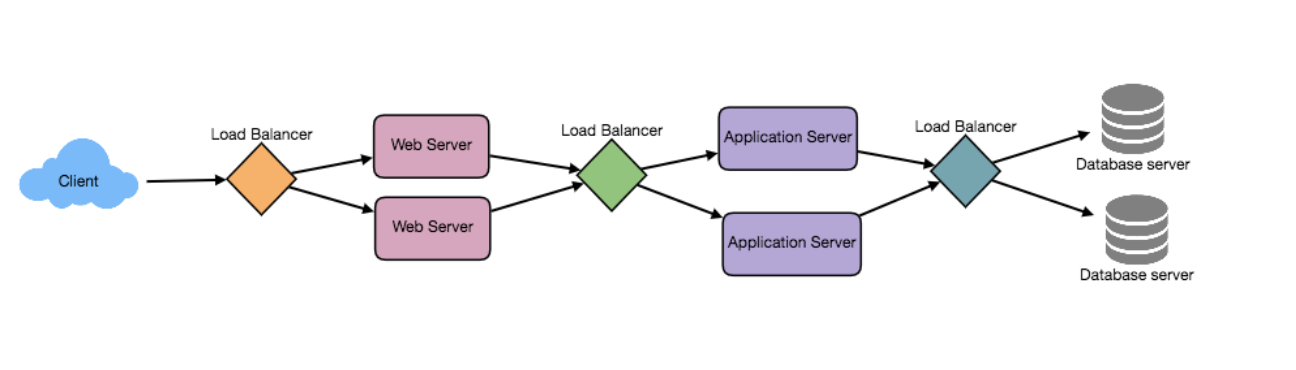
Benefits
- Users experience
faster,uninterruptedservice. Users won’t have to wait for a single struggling server to finish its previous tasks. Instead, their requests are immediately passed on to a more readily available resource. - Service providers experience
less downtimeandhigher throughput. Even a full server failure won’t affect the end user experience as the load balancer will simply route around it to a healthy server. - Load balancing makes it easier for
system administratorstohandle incoming requestswhile decreasing wait time for users. - Smart load balancers provide benefits like
predictive analyticsthatdetermine traffic bottlenecksbefore they happen. As a result, the smart load balancer gives an organization actionable insights. These are key to automation and can help drive business decisions. - System administrators experience
fewer failedorstressed components. Instead of a single device performing a lot of work, load balancing hasseveral devicesperform alittle bitof work.
Algorithms
How does the LB choose the backend server?
Load balancers consider two factors before forwarding a request to a backend server. They will first ensure that the server they choose is actually responding appropriately to requests and then use a pre- configured algorithm to select one from the set of healthy servers.
Health Checks
Load balancers should only forward traffic to “healthy” backend servers.
- Least Connection Method
- This method directs traffic to the server with the
fewest active connections. This approach is quite useful when there are a large number of persistent client connections which are unevenly distributed between the servers.
- This method directs traffic to the server with the
- Least Response Time Method
- This algorithm directs traffic to the server with the
fewest active connectionsand thelowest average response time.
- This algorithm directs traffic to the server with the
- Least Bandwidth Method
- This method selects the server that is currently serving the
least amount of traffic measured in megabits per second(Mbps).
- This method selects the server that is currently serving the
- Round Robin Method
- This method cycles through a list of servers and sends each new request to the next server.
When it reaches the end of the list, it starts over at the beginning. It is most useful when the servers are of equal specification and there are not many persistent connections.
- This method cycles through a list of servers and sends each new request to the next server.
- Weight Round Robin Method
- The weighted round-robin scheduling is designed to better handle servers with different processing capacities.
Each server is assigned a weight(an integer value that indicates the processing capacity). Servers withhigher weightsreceivenew connectionsbefore those with less weights and servers with higher weightsget more connectionsthan those with less weights.
- The weighted round-robin scheduling is designed to better handle servers with different processing capacities.
- IP Hash
- Under this method, a
hash of the IP addressof the client is calculated to redirect the request to a server.
- Under this method, a
Redundant Load Balancers
The load balancer can be a single point of failure; to overcome this, a second load balancer can be connected to the first to form a cluster. Each LB monitors the health of the other and, since both of them are equally capable of serving traffic and failure detection, in the event the main load balancer fails, the second load balancer takes over.
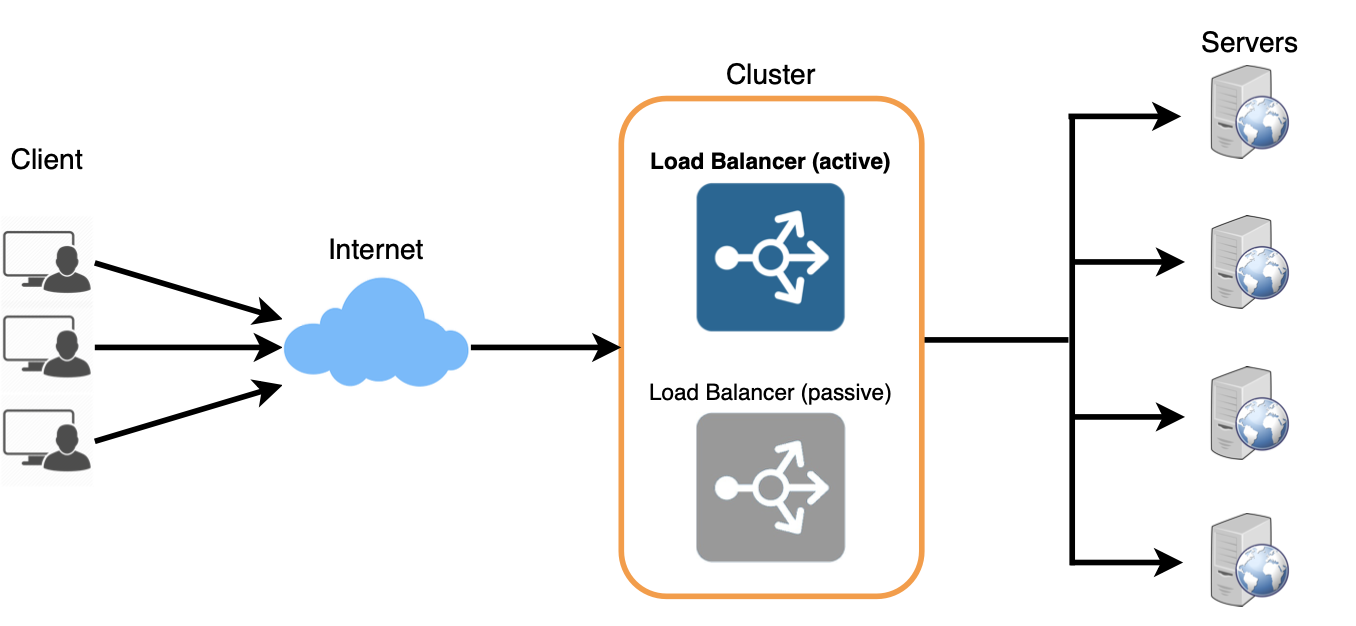
Reference
https://www.educative.io/courses/grokking-the-system-design-interview/3jEwl04BL7Q

Comments
Join the discussion for this article at here . Our comments is using Github Issues. All of posted comments will display at this page instantly.