Eulerian Path
In graph theory, an
Eulerian trail(orEulerian path) is a trail in a finite graph that visits every edge exactly once (allowing for revisiting vertices). Similarly, anEulerian circuitorEulerian cycleis an Eulerian trail that starts and ends on the same vertex.
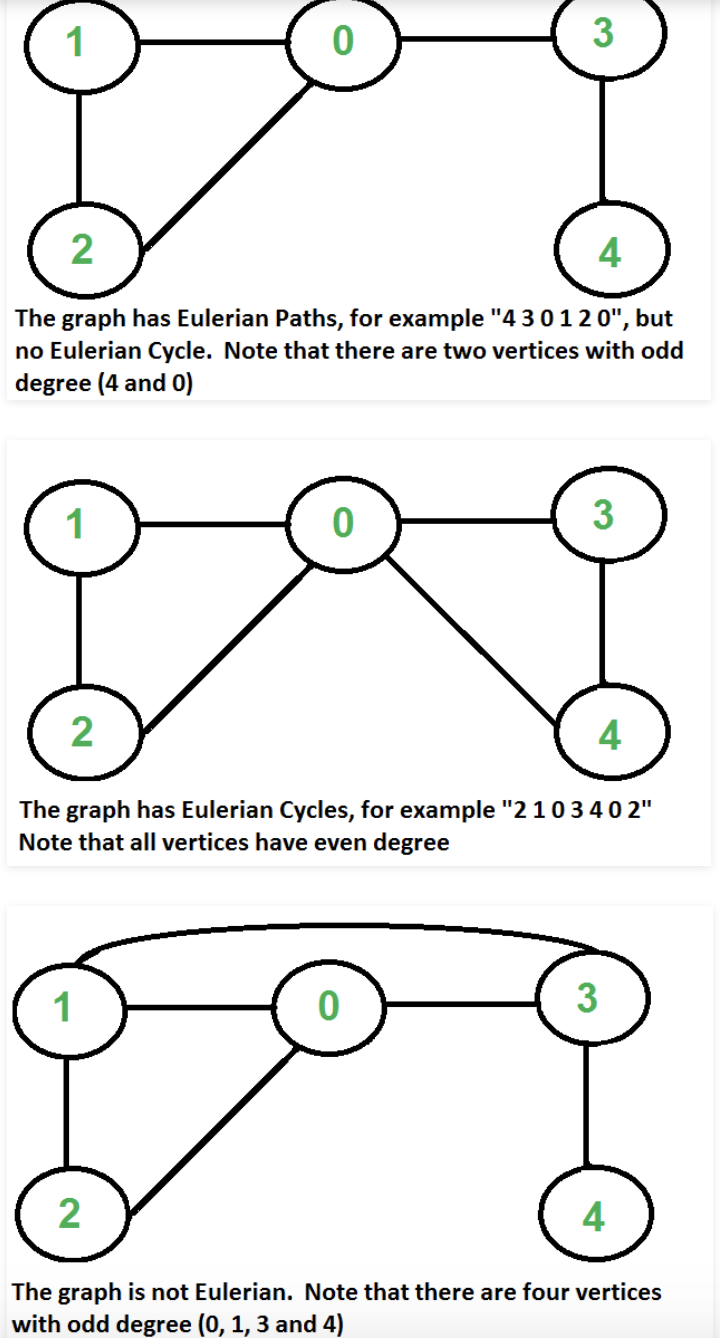
We could find whether a given graph has a Eulerian Path or not in polynomial time. In fact, we can find it in O(V+E) time.
Properties
Eulerian Cycle
An undirected graph has Eulerian cycle if following two conditions are true.
- All vertices with non-zero degree are connected. We don’t care about vertices with zero degree because they don’t belong to Eulerian Cycle or Path (we only consider all edges).
- All vertices have even degree.
Eulerian Path
An undirected graph has Eulerian Path if following two conditions are true.
- All vertices with non-zero degree are connected. We don’t care about vertices with zero degree because they don’t belong to Eulerian Cycle or Path (we only consider all edges).
- If two vertices have odd degree and all other vertices have even degree. Note that only one vertex with odd degree is not possible in an undirected graph (sum of all degrees is always even in an undirected graph)
Note: a graph with no edges is considered Eulerian because there are no edges to traverse.
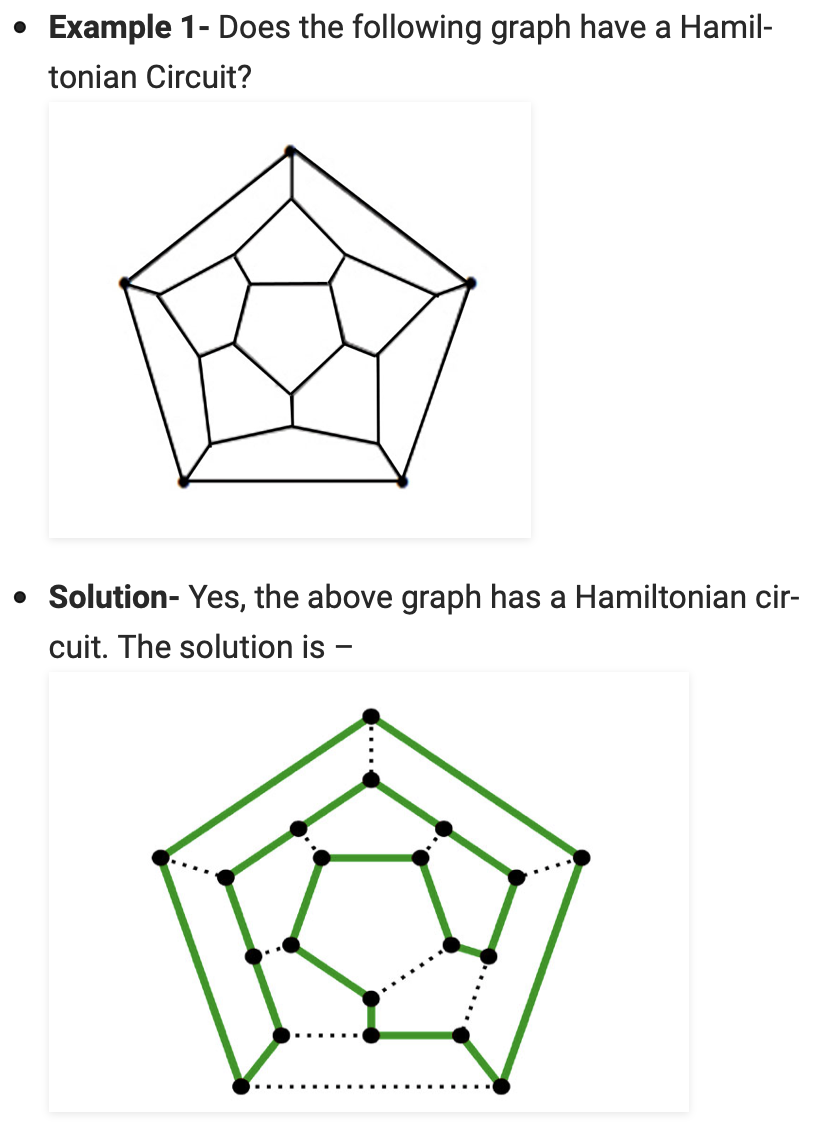
Hamiltonian Path
In the mathematical field of graph theory, a
Hamiltonian path(ortraceable path) is a path in an undirected or directed graph that visits each vertex exactly once. AHamiltonian cycle(orHamiltonian circuit) is a Hamiltonian path that is acycle.
Determin whether such paths and cycles exist in graph is the Hamiltonian path problem, which is NP-complete.
Reference
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Eulerian_path

Comments
Join the discussion for this article at here . Our comments is using Github Issues. All of posted comments will display at this page instantly.